Endocannabinoids, Brain Chemicals Similar To Marijuana
Memory, rest, reproduction, pleasure and even stress regulation… Endocannabinoids are fascinating molecules that the body produces to modulate the endocannabinoid system (SEC). If we were to say right now that a large part of the body is “flooded” by these chemical substances, it is possible that more than one would be surprised and concerned.
Nothing when it comes to biology and neurochemistry is accidental. These small substances are a key piece in the brain’s reward systems. Thanks to them we carry out multiple daily processes and any imbalance in their production can completely alter our well-being. In this sense, recent studies show how any alteration in endocannabinoids can mediate the processes of stress and anxiety.
It is also interesting to know that although these elements are endogenous – that is, they are produced by the brain – they can also be found in nature. Indeed, the marijuana plant also has these chemicals. However, and here comes the revealing fact that we should keep in mind, all of us already bring our own cannabinoid system “from the factory”.
Endocannabinoids, what are they?
It is true that endocannabinoids are one of the active components of the marijuana plant. Now, as we have already pointed out, the brain also produces them on a regular basis and they are present in the body and flowing in the bloodstream.
Endocannabinoids are basically lipid (fat) molecules that have an essential purpose when it comes to promoting communication between neurons. Research works such as those carried out in the department of psychological and brain sciences at the University of Indiana (United States) indicate something important.
To date, only two types of these chemicals have been identified, anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG). When they act on endocannabinoid receptors, multiple basic processes are regulated in our daily lives, such as learning, memory, sleep, appetite and even mood.
Likewise, and no less important, these molecules fulfill another essential function. AEAs and 2-AG modulate the brain’s reward circuits. They do this by stimulating the production of dopamine, in a way that not only regulates our motivation, but is also essential to mediate states of pleasure.
What functions do they have?
Although only two types of endocannabinoids have been identified, the truth is that it is suspected that there may be many more given their multiple functions.
On the other hand, and to understand how they work, it is important to remember that these endogenous cannabinoids are natural neurotransmitters. That is, they act as chemical messengers in the body that send signals between nerve cells. Let’s see its functions.
Regulate our energy
These biological components mediate night rest and activation as well. They are decisive to promote sleep, but in turn they can activate our motivation so that we experience pleasure when working towards a goal.
Stimulate the appetite
The central endocannabionid system is involved in a wide spectrum of physiological processes, appetite being one of the most important.
As a curious fact, science discovered years ago that the main psychoactive constituent of cannabis, Δ9-THC, acted on our endocannabinoid system, to increase the feeling of hunger in patients suffering from anorexia or even cancer.
Blood circulation
Among the two endocannabinoids discovered, 2-AG is one of the most important in the brain, liver, and lungs. What it does in these organs is produce arachidonic acid, which is used in the synthesis of prostaglandins. Thanks to them, functions such as blood pressure, blood clotting or even the allergic inflammatory response are carried out.
Pain regulation
Something remarkable that is worth knowing about the endocannabinoid system is that it is one of the key pieces in intercellular communication. As if that weren’t enough, it is also involved in a wide variety of physiological processes, such as the regulation of pain perception.
When the brain detects an inflammatory process or the presence of a wound or blow, endocannabinoids are immediately activated to reduce suffering.
Memory and learning
Neuroscience has been giving us important data on these chemical compounds for years. One of the most relevant is knowing that there are endocannabinoid receptors in the hippocampus and the cortex, which favors memory and learning processes.

The endocannabinoid system and pleasant social experiences
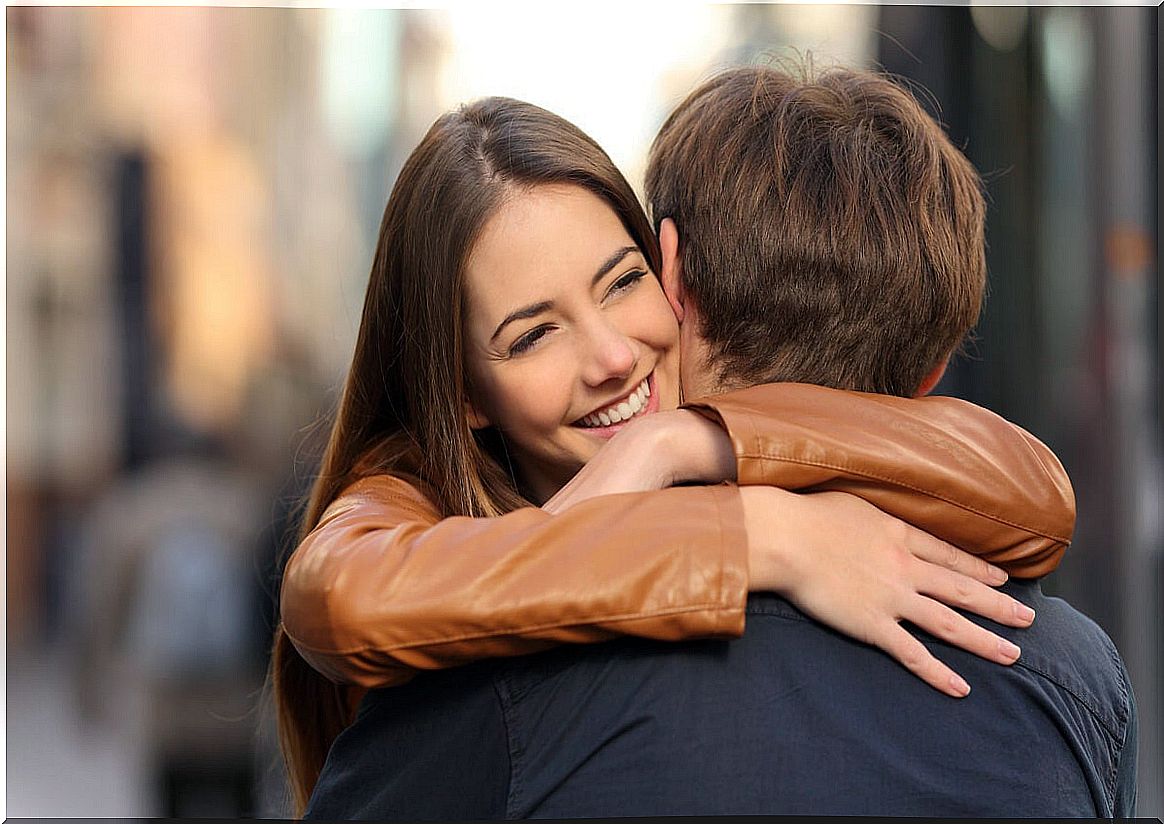
We pointed out at the beginning, the whole body is “flooded” by these chemical substances. Now, in a study published just a few days ago from the University of Muenster (Germany) they point out something remarkable. The endocannabinoids AEA and 2-AG are key to the pleasure we experience in everyday social relationships.
These endogenous chemicals facilitate the release of dopamine into the brain’s reward centers whenever we do something that the brain interprets as socially positive. A hug, a chat with our friends over coffee, a walk with the couple, playing with our children. ..
All this fills our bloodstream with those components similar to marijuana that generate pleasure, well-being and happiness. There is no better way to reduce stress and anxiety than to enjoy those moments of balance and complicity with those we love the most.









